.Introduction
In this work, we propose an efficient algorithm for MR image reconstruction. The algorithm minimizes a linear combination of three terms corresponding to a least square data fitting, total variation (TV) and L1 norm regularization. This has been shown to be very powerful for the MR image reconstruction. First, we decompose the original problem into L1 and TV norm regularization subproblems respectively. Then, these two subproblems are efficiently solved by existing techniques. Finally, the reconstructed image is obtained from the weighted average of solutions from two subproblems in an iterative framework. We compare the proposed algorithm with previous methods in term of the reconstruction accuracy and computation complexity. Numerous experiments demonstrate the superior performance of the proposed algorithm for compressed MR image reconstruction.
.Download
Junzhou Huang, Fei Yang, "Compressed Magnetic Resonace Imaging Based on Wavelet Sparsity and Nonlocal Total Variation". IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging, ISBI'12, Bacelona, Spain, May 2012. [PDF] [CODES]
Junzhou Huang, Shaoting Zhang and Dimitris Metaxas. " Efficient MR Image Reconstruction for Compressed MR Imaging ", In Proc. of the 13th Annual International Conf. on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention, MICCAI’2010, Beijing, China, September 2010. Best Student Paper Award. [PDF] [SLIDES] [CODES] [Supplemental]
Junzhou Huang, Shaoting Zhang, Dimitris Metaxas, "Efficient MR Image Reconstruction for Compressed MR Imaging", Medical Image Analysis, Volume 15, Issue 5, pp. 670-679, October 2011. [CODES]
Notice: The codes was tested on Windows and MATLAB 2008. If you have any suggestions or you have found a bug, please contact us via email at jzhuang@uta.edu
FCSA_MRI Algorithms
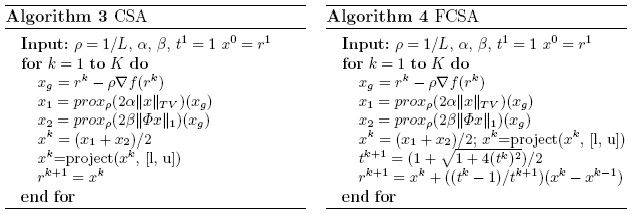 |
Figure.
Main steps of the proposed algorithm |
Visual Comparison
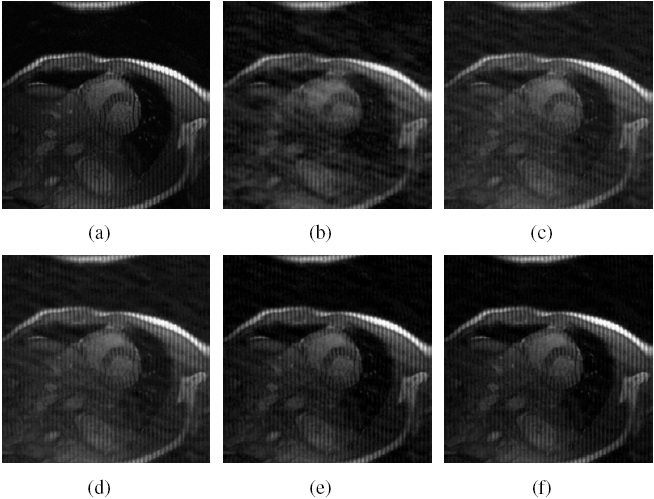 |
Figure.
Cardiac MR image reconstruction from
20% sampling (a) Original image; (b), (c), (d) (e) and (f)
are the reconstructed images by the CG [1], TVCMRI [2], RecPF
[3], CSA and FCSA. Their SNR are 9.86, 14.43, 15.20, 16.46
and 17.57 (db). Their CPU time are 2.87, 3.14, 3.07, 2.22
and 2.29 (s). |
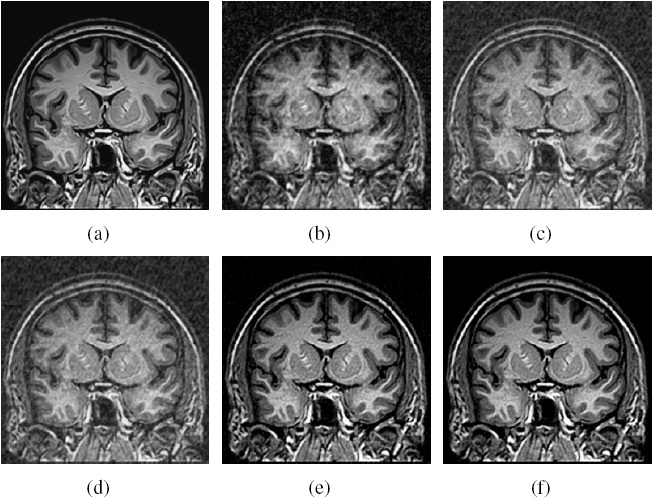 |
Figure.
Brain MR image reconstruction from 20%
sampling (a) Original image; (b), (c), (d) (e) and (f) are
the reconstructed images by the CG [1], TVCMRI [2], RecPF
[3], CSA and FCSA. Their SNR are 8.71, 12.12, 12.40, 18.68
and 20.35 (db). Their CPU time are 2.75, 3.03, 3.00, 2.22
and 2.20 (s). |
Performance Comparisons
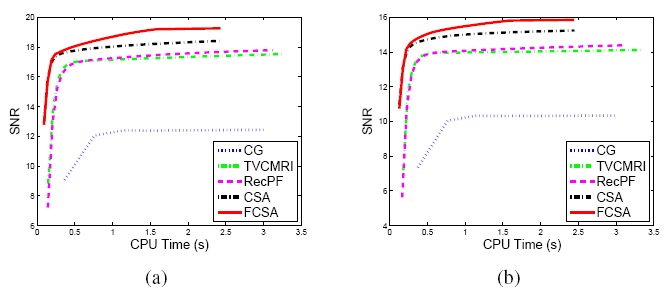 |
Figure.
Performance comparisons (CPU-Time vs. SNR) on different MR
images: a) Cardiac image and (b) Brain image. |
Related Sources
[1] SparseMRI
[2] TVMRI
[3] RecPF