Volume modeling, simulation and segmentation are important parts of computer based medical applications for diagonsis and analysis of anatomical data. With rapid advances in medical imaging modalities and volume visualization techniques, computer based diagnosis is becoming a reality. These computer based tools allow scientists and physicians to understand and diagnose anatomical structures by virtually interacting with them. 3D modeling, simulation and segmentaition play a critical role by facilitating automatic extraction and visualization of the anatomical organ or interested objects. We developed a 3D deformal model, Metamorphs, which integrates region texture constraints so as to achieve more robust segmentation. Compared with traditional shape-based models, Metamorphs segmentation result is less dependent on model initialization and not sensitive to noise and spurious edges inside the object of interest. Then, we further extend it Active Volume Model (AVM), a similar and improved approach for 3D segmentation. The shape of this 3D model is considered as an elastic solid, with a simplex-mesh surface made of thousands of vertices. Efficient optimization and fast convergence of the model are achieved using the Finite Element Method (FEM). To further improve segmentation performance, a multiple-surface constraint is also employed to incorporate spatial constraints among multiple objects. Several applications are shown to demonstrate the benefits of these segmentation algorithms based on deformable models that integrate multiple sources of constraints.
3D Modeling and Segmentation
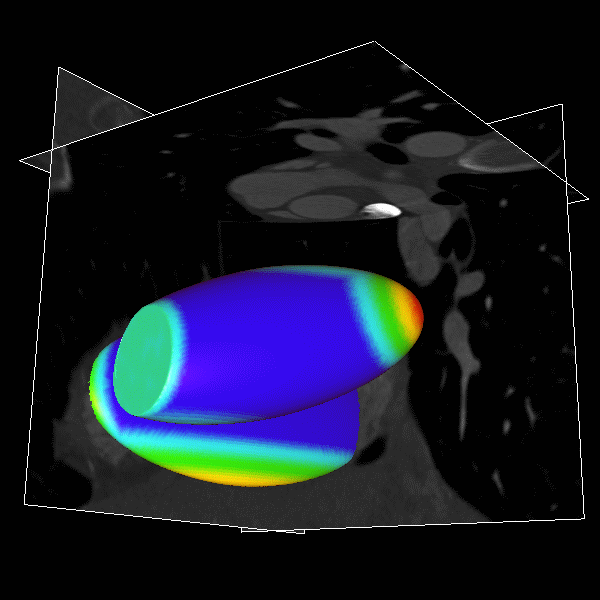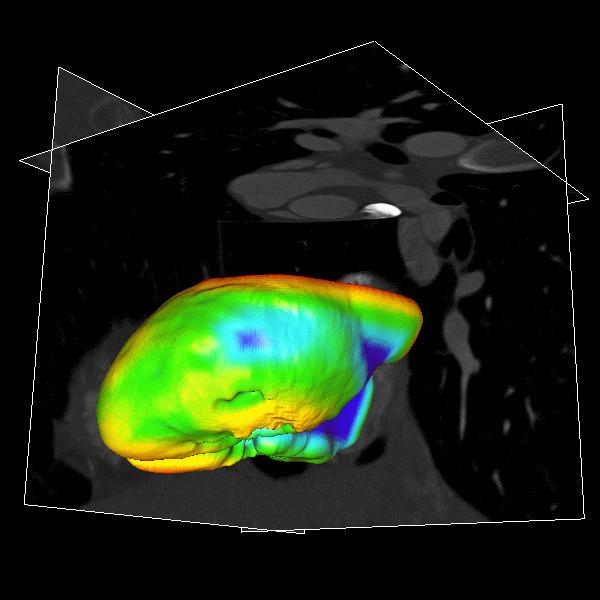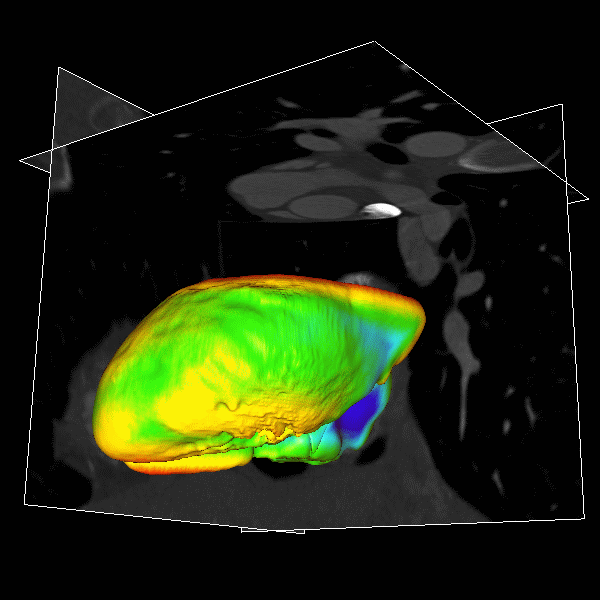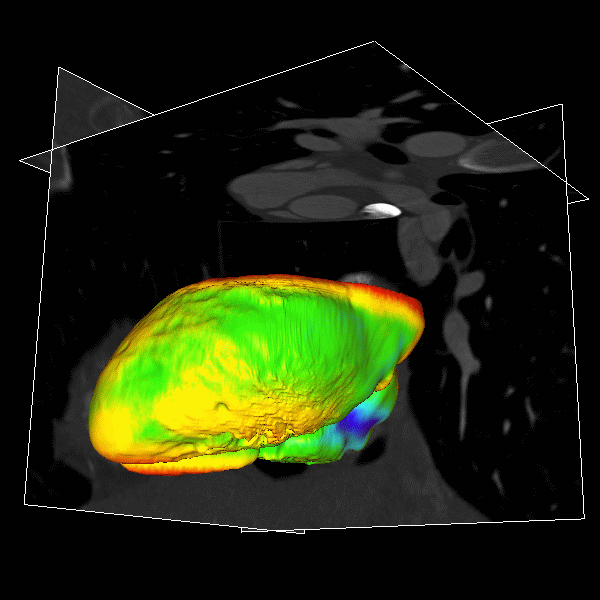
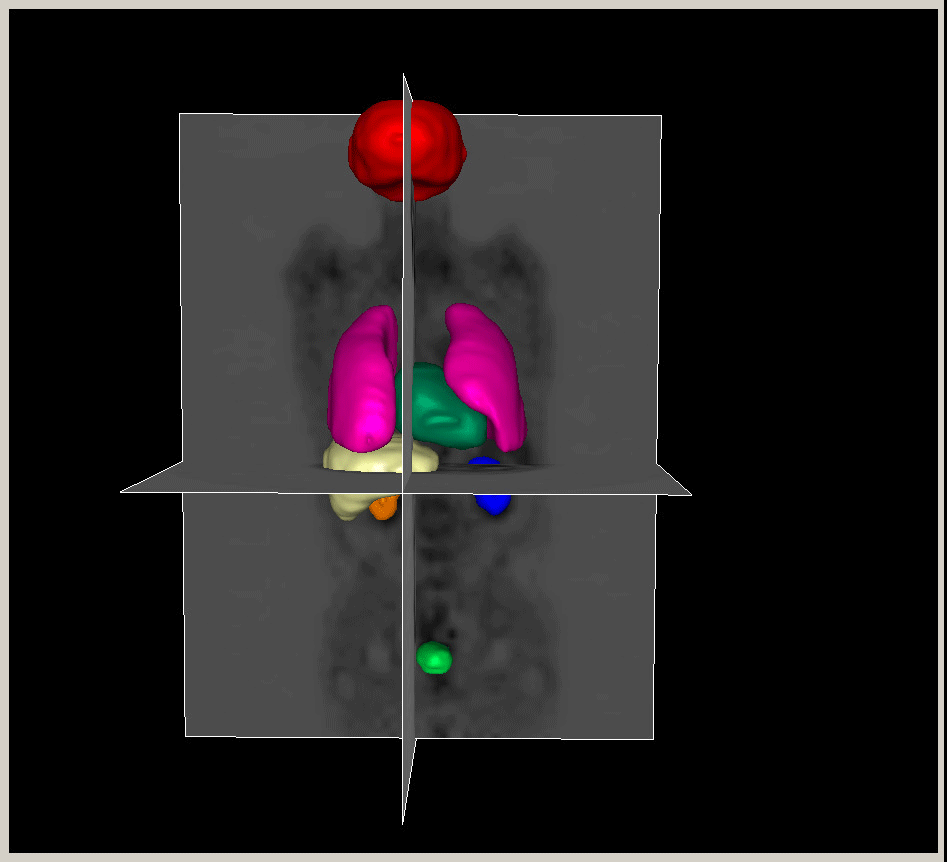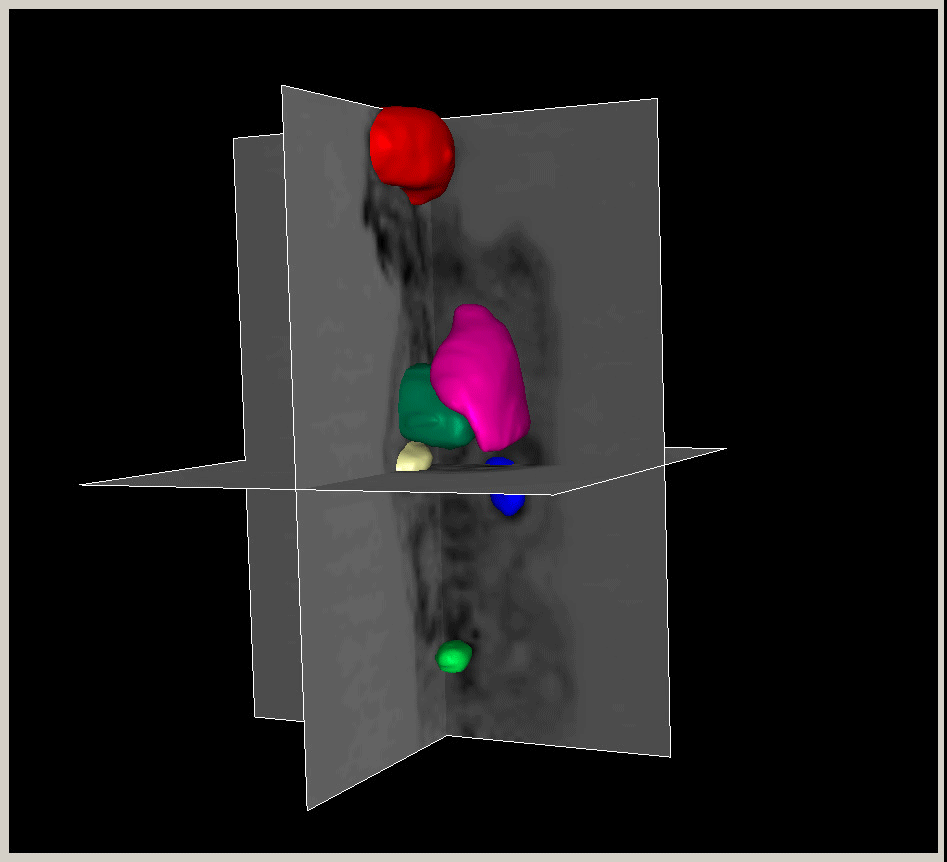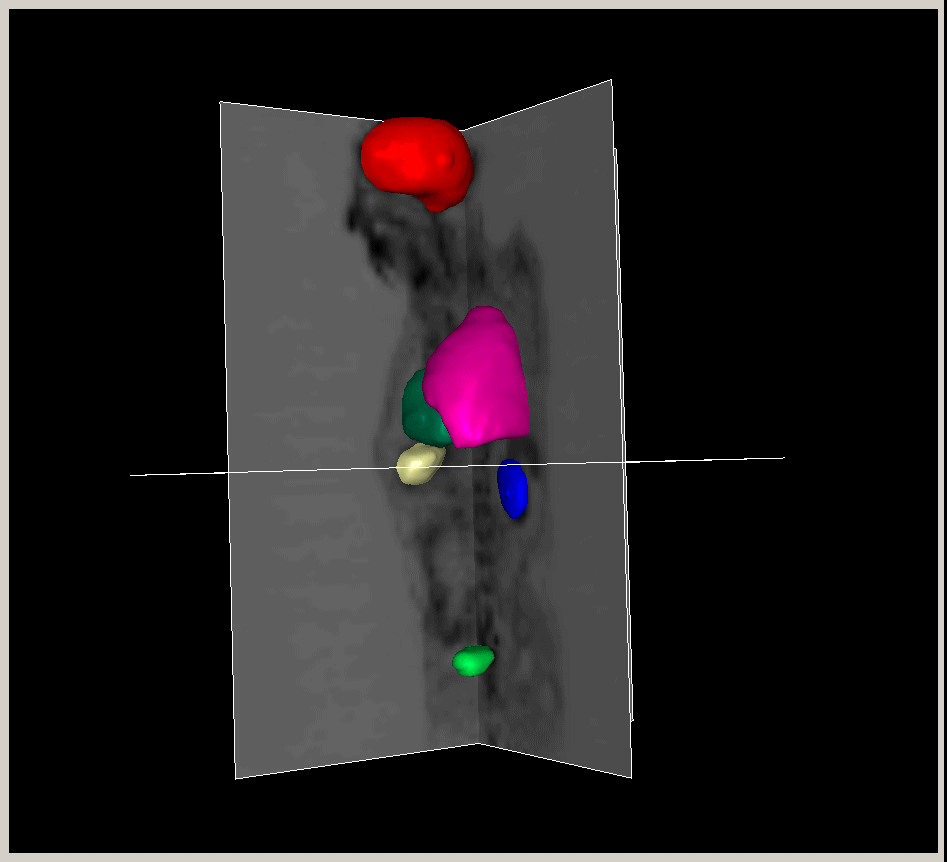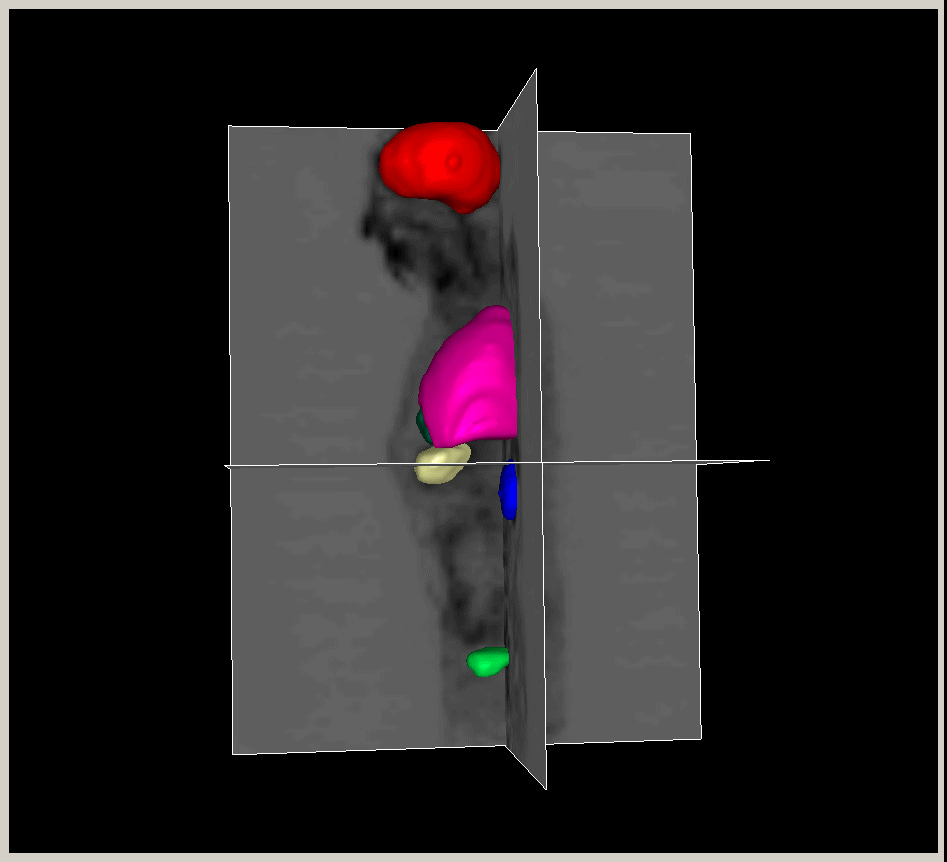
|
Figure.
3D modeling for Heart (Left), Lung (Middle) and multiple organs
in whole body (Right). |
3D Heart
|
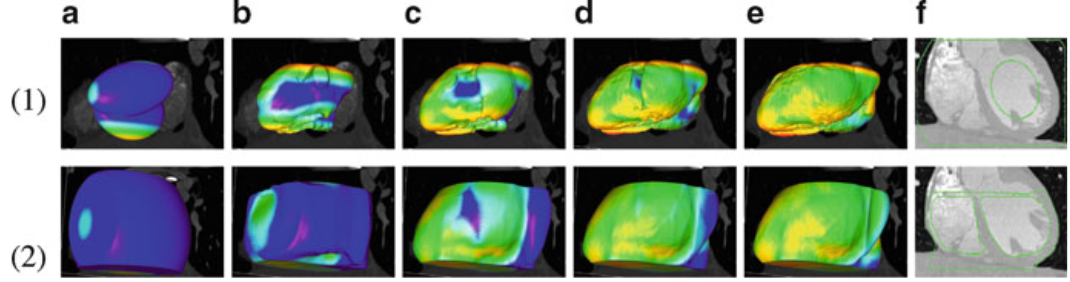
Figure.
3D heart surface segmentation; the distance range
is 2–25 voxels, (1) (a)–(e) deformation
progress of inner surfaces, (2) (a)–(e) outer
surface; (a) Initial model after (b) 3, (c) 9, (d)
21, (e) 27 (converged result) iterations; (1)(f) initial
model in a 2D slice, (2)(f ) converged result in a
2D slice. |
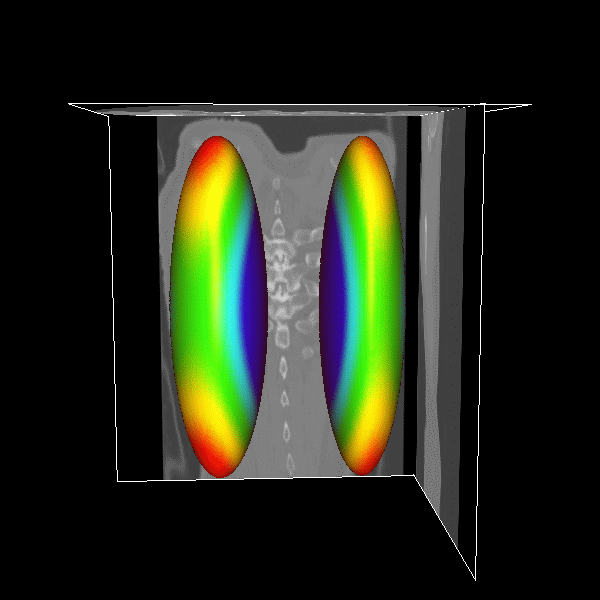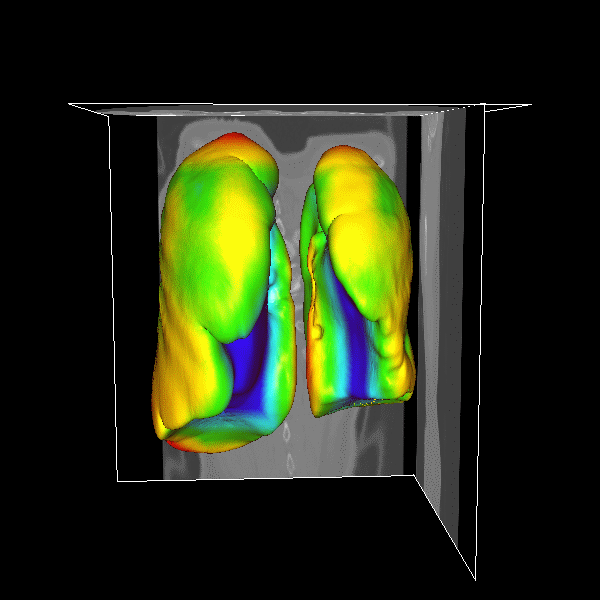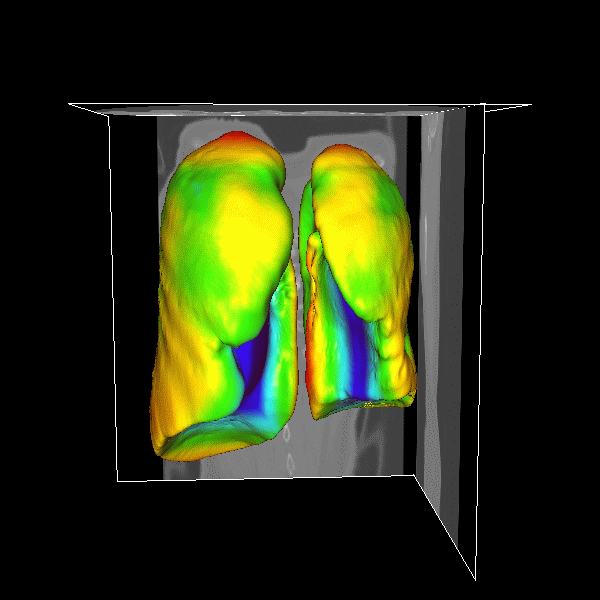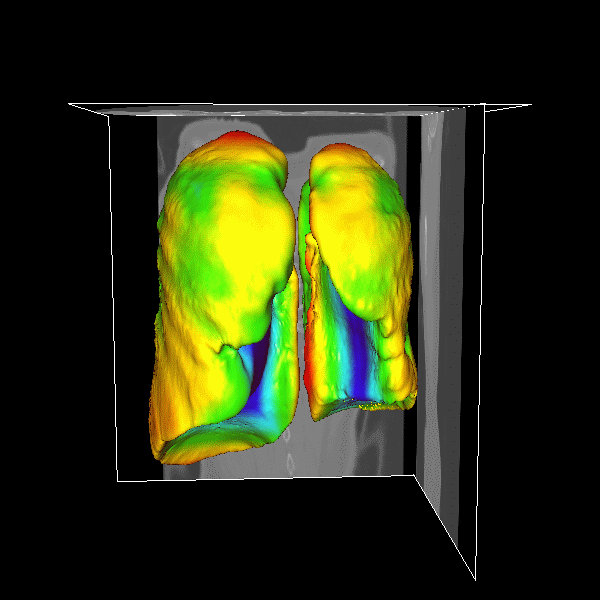
3D Lung
|
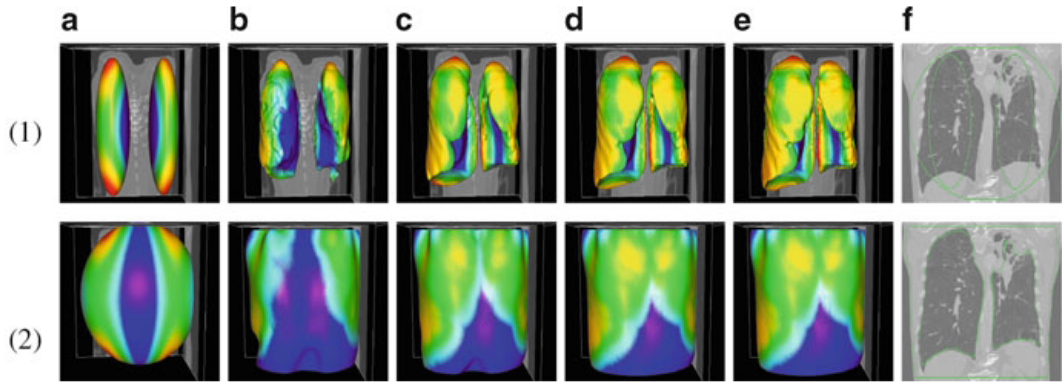
Figure.
3D lung surface segmentation; the distance range is
3–45 voxels, (1) (a)–(e) deformation progress
of inner surfaces, (2) (a)–(e) outer surface;
(a) Initial model after (b) 3, (c) 9, (d) 21, (e)
26 (converged result) iterations; (1)(f) initial model
in a 2D slice, (2)(f ) converged result in a 2D slice. |
3D Brain
|
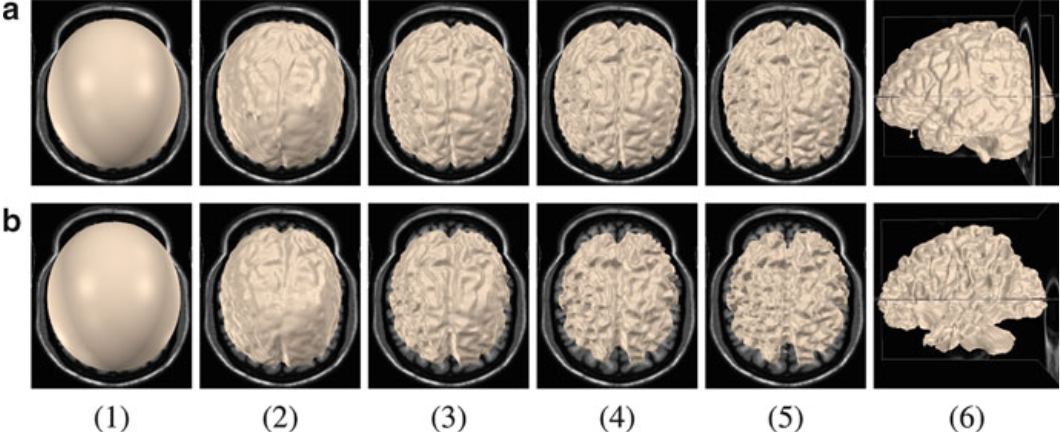
Figure.
GM and WM segmentation using AVM. The GM and
WM model surfaces each has 131,074 control vertices.
(a)(1) Initial model of GM, (2) after three
iterations, (3) after 12 iterations, (4) after
24 iterations, (5), (6) final converged result
after 36 iterations. (b)(1) Initial model of
WM, (2) after three iterations, (3) after 12
iterations, (4) after 24 iterations, (5), (6)
final converged result after 39 iterations |
Segmentation Comparison
|
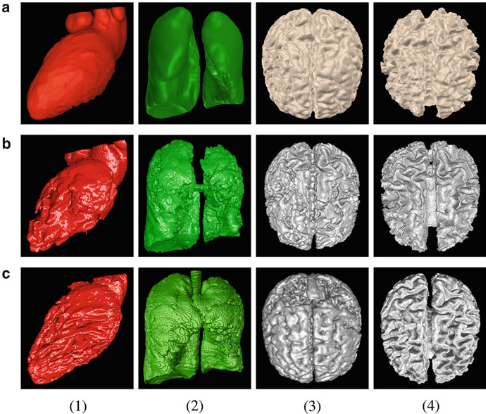
Figure.
Comparing AVM with geodesic active contours (GAC)
and level set evolution without reinitialization (LSEWR).
(a) AVM, (b) GAC, (c) LSEWR. (1) heart LV segmentation,
(2) lung segmentation, (3) brain GM segmentation,
(4) brain WM segmentation. |
Segmentation Demos
Figure.
Segmentation Demos: (left) 3D liver segmentation
in low-dose CT; (right) 3D Rodent Rain Segmentation
in MRM. |
.Publications
-
Shaoting Zhang, Yiqiang Zhan, Xinyi Cui, Mingchen Gao, Junzhou Huang, Dimitris Metaxas, "3D Anatomical Shape Atlas Construction using Mesh Quality Preserved Deformable Models", Computer Vision and Image Understanding, Special Issue on Shape Modeling in Medical Image, 2013.
-
Yang Yu, Shaoting Zhang, Junzhou Huang, Dimitris Metaxas and Leon Axel, "Sparse Deformable Models with Application to Cardiac Motion Analysis", In Proc. of the 23rd biennial International Conference on Information Processing in Medical Imaging, IPMI'13, Asilomar, CA, June 2013.
-
Lin Zhong, Shaoting Zhang, Mingchen Gao, Junzhou Huang, Zhen Qian, Dimitris Metaxas and Leon Axel, "Papillary Muscles Analysis from High Resolution CT using Spatial-Temporal Skeleton Extraction", In Proc. of the IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging, ISBI'13, San Francisco, CA, USA, April 2013.
-
Shaoting Zhang, Yiqiang Zhan, Maneesh Dewan, Junzhou Huang, Dimitris Metaxas and Xiang Zhou, "Toward Robust and Effective Shape Modeling: Sparse Shape Composition", Medical Image Analysis, Volume 16, Issue 1, pp. 265-277, January 2012.
-
Xinyi Cui, Shaoting Zhang, Junzhou Huang, Xiaolei Huang and Dimitris Metaxas, Leon Axel, "Left Endocardium Segmentation using Spatio-temporal Metamorphs", In Proc. of the IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging, ISBI'12, Barcelona, Spain, May 2012.
-
Tian Shen, Shaoting Zhang, Junzhou Huang, Xiaolei Huang and Dimitris Metaxas, "Integrating Shape and Texture in 3D Deformable Models: From Metamorphs to Active Volume Models", book chapter, In Multi Modality State-of-the-Art Medical Image Segmentation and Registration Methodologies, Springer, 2011.
-
Shaoting Zhang, Junzhou Huang and Dimitris Metaxas, "Robust Mesh Editing Using Laplacian Coordinates", Graphical Models, Volume 73, Issue 1, pp.10-19, January 2011.
-
Tian Shen, Xiaoleo Huang, Hongsheng Li, Edward Kim, Shaoting Zhang and Junzhou Huang, "A 3D Laplacian-Driven Parametric Deformable Model", In Proc. of the 13th International Conference on Computer Vision, ICCV'11, Barcelona, Spain, November 2011.
-
Shaoting Zhang, Junzhou Huang, Mustafa Uzunbas, Tian Shen, Foteini Delis, Xiaolei Huang, Nora Volkow, Panayotis Thanos and Dimitris N. Metaxas, "3D Segmentation of Rodent Brain Structures Using Hierarchical Shape Priors and Deformable Models", In Proc. of the 14th Annual International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention, MICCAI'11, Toronto, Canada, September 2011.
-
Shaoting Zhang, Yiqiang Zhan, Maneesh Dewan, Junzhou Huang, Dimitris Metaxas and Xiang Zhou, "Deformable Segmentation via Sparse Shape Composition: Towards the Robustness to Weak Appearance Cues", In Proc. of the 14th Annual International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention, MICCAI'11, Toronto, Canada, September 2011. (MICCAI Young Scientist Award Finalist)
-
Shaoting Zhang, Yiqiang Zhan, Maneesh Dewan, Junzhou Huang, Dimitris Metaxas and Xiang Zhou, "Sparse Shape Composition: A New Framework for Shape Prior Modeling", In Proc. of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR'11, Colorado Springs, Colorado, USA, June 2011.
-
Mingchen Gao, Junzhou Huang, Shaoting Zhang, Zhen Qian, Szilard Voros, Dimitri Metaxas, Leon Axel, "4D Cardiac Reconstruction Using High Resolution CT Images", In Proc. of the Sixth International Conference on Functional Imaging and Modeling of the Heart, FIMH'11, New York, USA, May 2011. (Best Paper Award)
-
Shaoting Zhang, Mustafa Uzunbas, Zhennan Yan, Mingchen Gao, Junzhou Huang, Dimitri Metaxas, Leon Axel, "Construction of Left Ventricle 3D Shape Atlas from Cardiac MRI", In Proc. of the Sixth International Conference on Functional Imaging and Modeling of the Heart, FIMH'11, New York, USA, May 2011.
-
Shaoting Zhang, Junzhou Huang, Mustafa Uzunbas, Tian Shen, Foteini Delis, Xiaolei Huang, Nora Volkow, Panayotis Thanos, Dimitris Metaxas, "3D Segmentation of Rodent Brain Structures Using Active Volume Model With Shape Priors", In Proc. of IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging: From Nano to Macro, ISBI'11, Chicago, Illinois, USA, March 2011.
-
Shaoting Zhang, Junzhou Huang and Dimitris Metaxas, "Robust Mesh Editing Using Laplacian Coordinates", Graphical Models, Volume 73, Issue 1, pp.10-19, January 2011.
-
Tian Shen, Yaoyao Zhu, Xiaolei Huang, Junzhou Huang, Dimitris Metaxas, Leon Axel, "Active Volume Models with Probabilistic Object Boundary Prediction Module", In Proc. of the 11th Annual International Conf. on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention, MICCAI’08, LNCS-5241, pp. 331-341, 2008.
-
Junzhou Huang, Xiaolei Huang, Dimitris Metaxas, and Leon Axel, "Adaptive Metamorphs Model for 3D Medical Image Segmentation", In Proc. of the 10th Annual International Conf. on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention, MICCAI’07, pp. 302-310, 2007